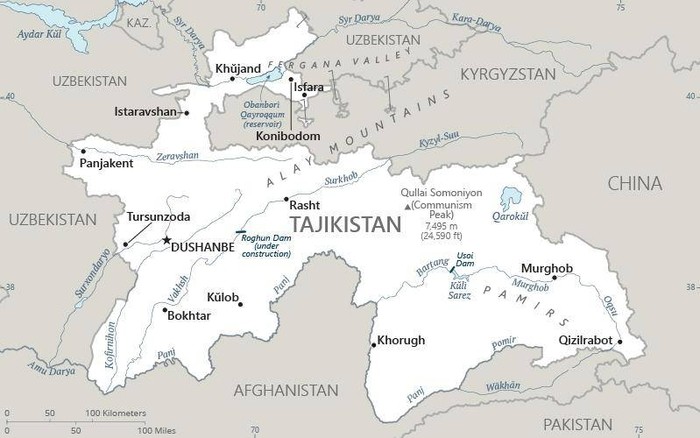
Tajikistan
Background:
The Tajik people came under Russian imperial rule in the 1860s and 1870s, but Russia’s hold on Central Asia weakened following the Revolution of 1917. Tajikistan became independent in 1991 following the breakup of the Soviet Union, and experienced a civil war between political, regional, and religious factions from 1992 to 1997. Though the country holds general elections for both the presidency (once every seven years) and legislature (once every five years), observers note an electoral system rife with irregularities and abuse, with results that are neither free nor fair. Tajikistan became a member of the WTO in March 2013. However, its economy continues to face major challenges, including dependence on remittances from Tajikistani migrant laborers working in Russia and Kazakhstan, pervasive corruption, and the opiate trade and other destabilizing violence emanating from neighboring Afghanistan.
Location:
Central Asia, west of China, south of Kyrgyzstan
Area:
144,100 sq km
Climate:
Mid-latitude continental, hot summers, mild winters; semiarid to polar in Pamir Mountains
Ethnic groups:
Tajik 84.3% (includes Pamiri and Yagnobi), Uzbek 13.8%, other 2% (includes Kyrgyz, Russian, Turkmen, Tatar, Arab) (2014 est.)
Languages:
Tajik (official) 84.4%, Uzbek 11.9%, Kyrgyz 0.8%, Russian 0.5%, other 2.4% (2010 est.)
Religions:
Muslim 98% (Sunni 95%, Shia 3%) other 2% (2014 est.)
Population:
9,119,347 (2022 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years: 31.43% (male 1,420,271/female 1,368,445)
15-24 years: 18.13% (male 816,658/female 792,231)
25-54 years: 40.58% (male 1,789,271/female 1,811,566)
55-64 years: 6.23% (male 253,862/female 299,378)
65 years and over: 3.63% (male 132,831/female 189,156) (2020 est.)
Government type:
Presidential republic
Capital:
Dushanbe
Time difference:
UTC+5 (10 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
Independence:
9 September 1991 (from the Soviet Union)
Economy – overview:
Tajikistan is a poor, mountainous country with an economy dominated by minerals extraction, metals processing, agriculture, and reliance on remittances from citizens working abroad. Mineral resources include silver, gold, uranium, antimony, tungsten, and coal. Industry consists mainly of small obsolete factories in food processing and light industry, substantial hydropower facilities, and a large aluminum plant – currently operating well below its capacity. The 1992-97 civil war severely damaged an already weak economic infrastructure and caused a sharp decline in industrial and agricultural production. Today, Tajikistan is the poorest among the former Soviet republics. Because less than 7% of the land area is arable and cotton is the predominant crop, Tajikistan imports approximately 70% of its food. Because of a lack of employment opportunities in Tajikistan, more than one million Tajik citizens work abroad – roughly 90% in Russia – supporting families back home through remittances that in 2017 were equivalent to nearly 35% of GDP.
GDP (purchasing power parity):
$34.88 billion (2020 est.)
GDP – per capita (PPP):
$3,700 (2020 est.)
Source:
CIA World Factbook